Tape, made of long strips of adhesive materials, is primarily used for a wide range of bonding and fastening applications, though it has several other applications as well. Typical tape applications include: fastening, sealing, bonding and binding. More specifically, tape products are used for: mending, protecting, jacketing, labeling, decorating, surfacing, surface marking and color coding. Read More…
Carolina Tape & Supply Co. is a distributor & custom tapes converter offering 100% satisfaction. As one of the leading tape suppliers in the nation, Carolina offers an array of quality products & services to your company.
CS Hyde is a leading distributor and converter that supplies a wide variety of high performance tapes with pressure sensitive adhesive. Our tape is available in materials such as Teflon™ Fluoroplastic, Kapton®, UHMW, Silicone, and many more. Since our fouding in 1996, our team at CS Hyde has continued to be committed to our customers and building long-term relationships by providing top...
CFS produces industrial masking products and flexible, converted materials such as gaskets, spacers, thermal pads, and EMI shielding for finishers, OEMs, and related suppliers. Please visit customfabricate.com to request information or to browse our selection of products online.
As a tape supplier our products serve many diverse industries such as aerospace, artistry, graphic arts, food and drink as well as many others! For over forty years we have been providing the highest quality tape products with the widest selection. Just a few examples of the products we offer are 3M masking, Teflon, gaffers tape as well as many others. To learn more about what we may be able to...
Budnick Converting is a family-owned custom converter and distributor of adhesive tapes, foams, and other flexible materials. We have over 70 years of experience in the tape and converting industry and offer adhesive tapes, foams, films, foils, and other specialty materials from every major manufacturer. Our primary converting services include slitting, die-cutting, printing, spooling,...
At Penmar Industries, we take pride in being trusted tape suppliers dedicated to providing adhesive solutions that meet the demands of modern industry. We supply an extensive range of pressure-sensitive tapes, including packaging, masking, double-coated, and specialty tapes, designed to deliver reliable performance in even the most challenging applications.

More Tape Suppliers
Adhesive tape products are vital solutions across countless industries and everyday situations. Common applications for tape include: aerospace engineering and assembly, arts and crafts projects, automotive manufacturing and repair, commercial and industrial packaging, construction, electrical and wiring insulation, furniture manufacturing, healthcare and medical uses, kitchen and food packaging, office supply, general manufacturing, painting, and sports and recreation.
The History of Tape
Adhesive tape, a cornerstone of modern bonding technology, traces its lineage to ancient adhesives. As early as 70,000 BC, South African cave dwellers combined red ochre and tree sap to seal cave paintings, foreshadowing basic adhesive chemistry. By 2000 BC, the Egyptians had documented glue recipes, while the Chinese (618–906 BC) refined animal glue from stag horn and fish bladder for surface bonding. For centuries, animal-based glues such as horse glue dominated, especially in the 1700s, until the advent of synthetic adhesives revolutionized bonding materials in the modern era.
The modern tape industry began in 1845 when Dr. Horace Day created the first adhesive tape, known as surgical tape, by combining a rubber-based adhesive with fabric strips. This innovation provided the foundation for today’s pressure-sensitive adhesives. Surgical tape led the market for 50 years, until 1901, when German inventor Oscar Troplowitz launched Leukoplast—an adhesive patch distributed by Beiersdorf AG—further advancing wound care and medical tape applications.
Major tape innovations continued in the 20th century. In 1921, Earle Dickson, an employee at Johnson & Johnson, invented the Band-Aid after his wife’s surgical tape failed to stay on her fingers. By bonding gauze to cloth-backed tape and covering it with crinoline, Dickson produced a reliable wound dressing. Johnson & Johnson quickly recognized the product’s value, promoted Dickson, and mass-produced Band-Aids—making adhesive bandages a household staple.
The invention of masking tape in 1925 by Richard Drew at 3M marked a breakthrough for the automotive and painting industries. Aimed at helping auto manufacturers achieve clean lines on two-tone cars, this pressure-sensitive tape later became known as Scotch Tape. 3M evolved into a global leader in adhesive tape manufacturing, offering a diverse range of tape products.
During World War II, Johnson & Johnson developed duct tape in 1942 to repair and waterproof soldiers’ ammunition cases. This versatile, water-resistant tape soon found utility beyond the battlefield, becoming a staple for both industrial and consumer applications. Advances in materials science and fabrication methods have since led to the development of specialty tapes, including double-sided tape, ultra-strong adhesives, and ultra-thin tape options for demanding applications.
Design
Production Process
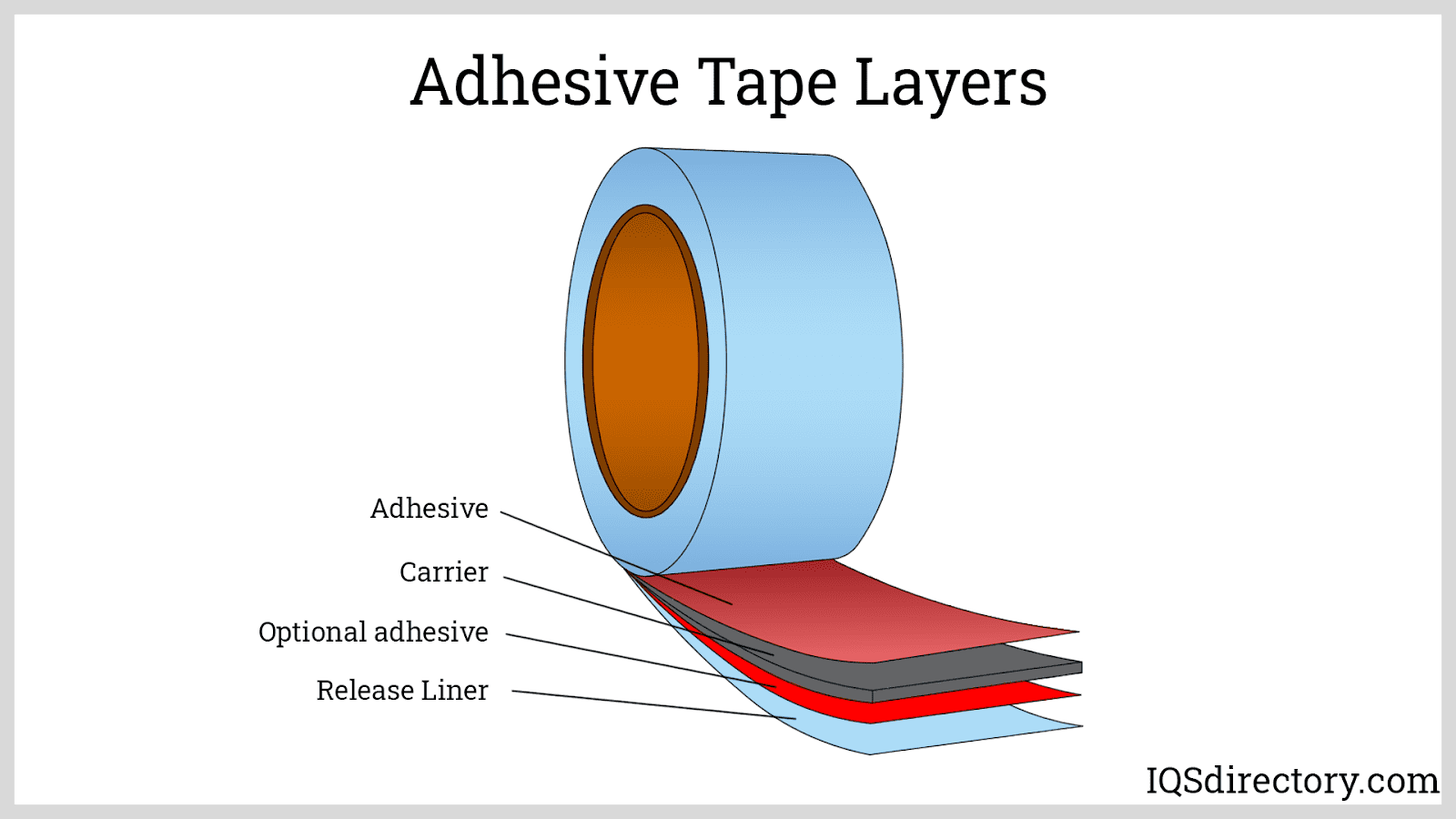
The manufacturing of adhesive tape involves combining a carrier material with a bonding adhesive to form a flexible, reliable product. Tape manufacturers employ a process known as “coating,” where adhesive is applied to a carrier substrate. The three primary coating methods are water-based coating, solvent coating, and hot-melt coating—each suited to specific tape types and performance requirements.
Water-Based Coating: Adhesives are mixed with water to form emulsions, producing a stable solution that is then coated onto carrier materials such as paper, films, or foils. Water-based tapes are valued for their environmental friendliness and are commonly used for packaging, masking, and general-purpose applications.
Solvent Coating: In this method, adhesives are dissolved in a solvent to lower viscosity and improve application. The adhesive solution is coated onto the carrier, then passed through a heated oven to evaporate the solvent, leaving a uniform adhesive layer. Solvent-based coatings excel in producing tapes with superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for electrical, automotive, and industrial uses.
Hot-Melt Coating: This process heats adhesive until it melts, then applies it to the carrier material. The adhesive solidifies as it cools, creating a fast and efficient production method. Hot-melt adhesives provide excellent initial tack and are widely used for carton sealing, packaging, and crafting tapes.
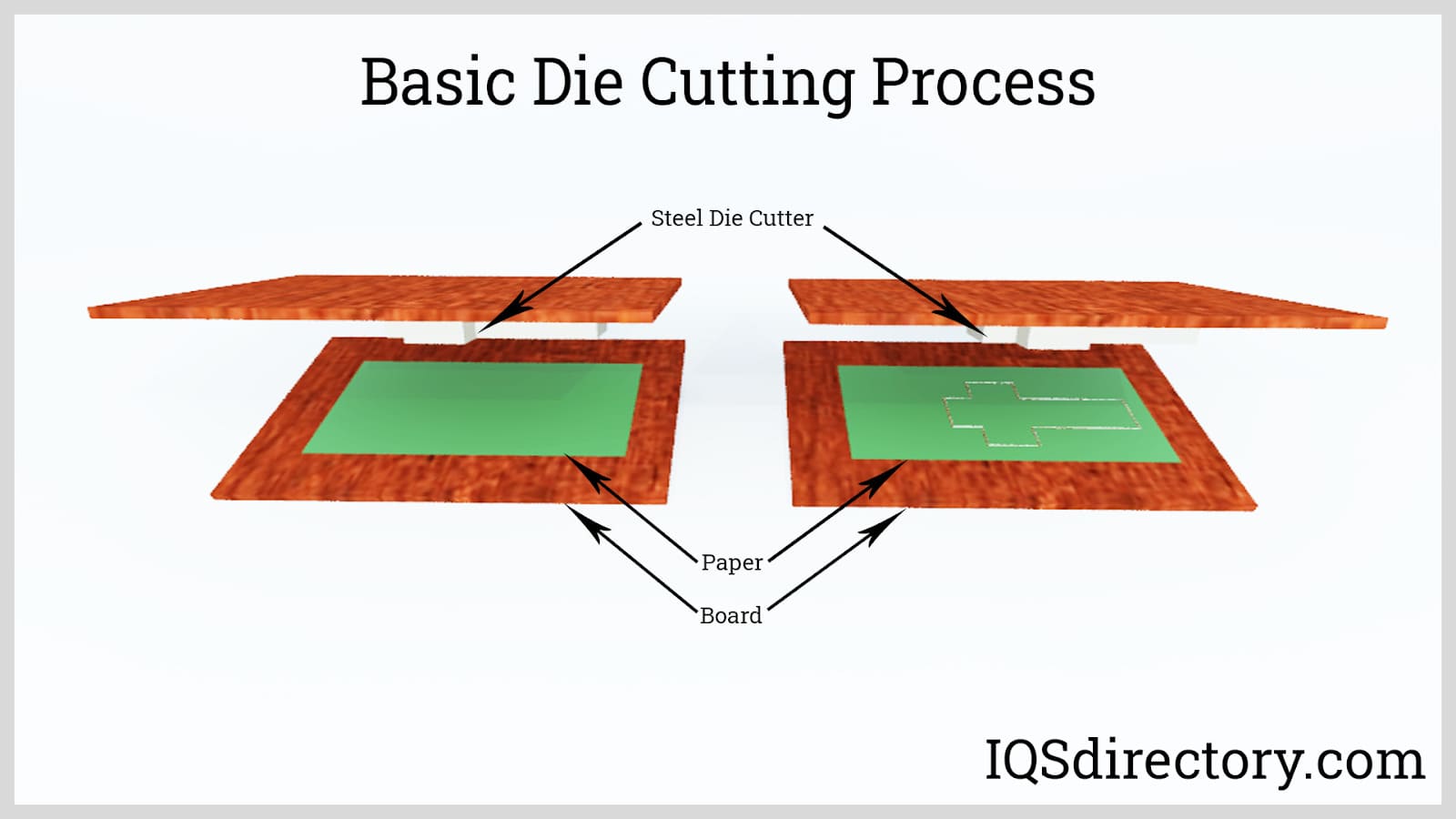
After coating, tape rolls may undergo converting processes such as winding into jumbo rolls, slitting into narrow widths, die cutting for custom shapes, or printing for branded and instructional tapes. These finishing steps ensure tapes are tailored for consumer, commercial, or industrial use and are ready for distribution by tape suppliers and wholesale distributors.
Materials
The choice of carrier and adhesive materials drastically affects tape performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Carrier substrates include:
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride): Offers flexibility, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation; commonly used in electrical and vinyl tapes.
- EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer): Provides durability and weather-resistance for outdoor tape applications.
- PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene): Known for nonstick, high-temperature, and chemical-resistant properties for specialty tapes.
- Aluminum and copper foil: Used in conductive and shielding tapes for electronics, HVAC, and aerospace industries.
- Polylactic acid and cellulose acetate: Biodegradable options for eco-friendly tape products.
- Paper, tissue, and films: Lightweight, conformable, and printable substrates for masking and general-purpose tapes.
Adhesives include acrylic, rubber, silicone, hot-melt, epoxy, and specialty formulas for electronics or medical-grade tapes. Selecting the right adhesive type determines tack, holding power, peel strength, and environmental resistance. For instance, silicone adhesives endure extreme temperatures, while acrylic adhesives offer UV stability and long-term reliability.
Considerations and Customization
Leading tape manufacturers and suppliers offer custom tape production to meet exacting requirements in industrial, commercial, or specialized consumer applications. When specifying custom tape solutions, consider these factors:
- Adhesion strength: Match the tape’s bonding power to the application—whether temporary or permanent, lightweight or heavy-duty.
- Surface compatibility: Ensure the adhesive is suitable for the substrate material, such as metal, glass, plastic, painted, or sensitive surfaces.
- Environmental requirements: Factor in exposure to moisture, chemicals, UV, temperature extremes, or sterilization (for medical tapes).
- Size and form: Choose the ideal tape width, thickness, roll length, sheet size, or die-cut shape for your application.
- Color and printing: Opt for colored tapes for coding, marking, or branding, and request custom printing for instructions or safety information.
- Dispenser and packaging: Select tape-only, tape-with-dispenser, or pre-cut forms, as well as bulk or retail packaging.
- Certifications: Seek tapes that comply with relevant ISO, ASTM, or industry standards for quality assurance.
When should you consider custom tape manufacturing? If you have unique operational needs, regulatory compliance requirements, or branding objectives, partnering with a supplier offering tailored adhesive tape solutions delivers better performance and value. Looking for a specific type of industrial tape or have custom adhesive needs? Browse our tape supplier listings to find a partner who can deliver to your exact specifications.
Types of Tape
Adhesive tapes are categorized by their adhesive mechanism, carrier material, intended use, and specialty features. This section explores the most widely used types, their benefits, and key buying considerations.
Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Tapes
Pressure-sensitive tapes (PSA tapes) are activated by applying light pressure, forming a durable bond with a variety of substrates. They require no heat, solvent, or water to adhere, making them user-friendly and versatile. Popular examples include:
- Duct tape: Renowned for its strength, flexibility, and water resistance. Suitable for HVAC, emergency repairs, patching, and even industrial sealing. Duct tape’s robust adhesive makes it a go-to choice for both DIY and professional applications, including military and aerospace repairs.
- Masking tape: Features an easy-release, easy-tear adhesive, ideal for painting, labeling, bundling, and general household tasks. Masking tape comes in various adhesion levels and is designed for clean removal from surfaces.
- Packaging tape: Engineered for sealing cartons, envelopes, and shipping boxes. It offers high tensile strength and secure adhesion to prevent package tampering or accidental opening during transit. Packaging tape is indispensable for e-commerce, warehouses, and logistics operations.
- Electrical tape: Made of non-conductive materials, electrical tape insulates and protects wires and cables. It withstands temperature fluctuations and resists abrasion, making it essential for electricians, installers, and maintenance personnel.
Material-Specific and Specialty Tapes
Tapes can also be classified by the material of their carrier or by specialized functions:
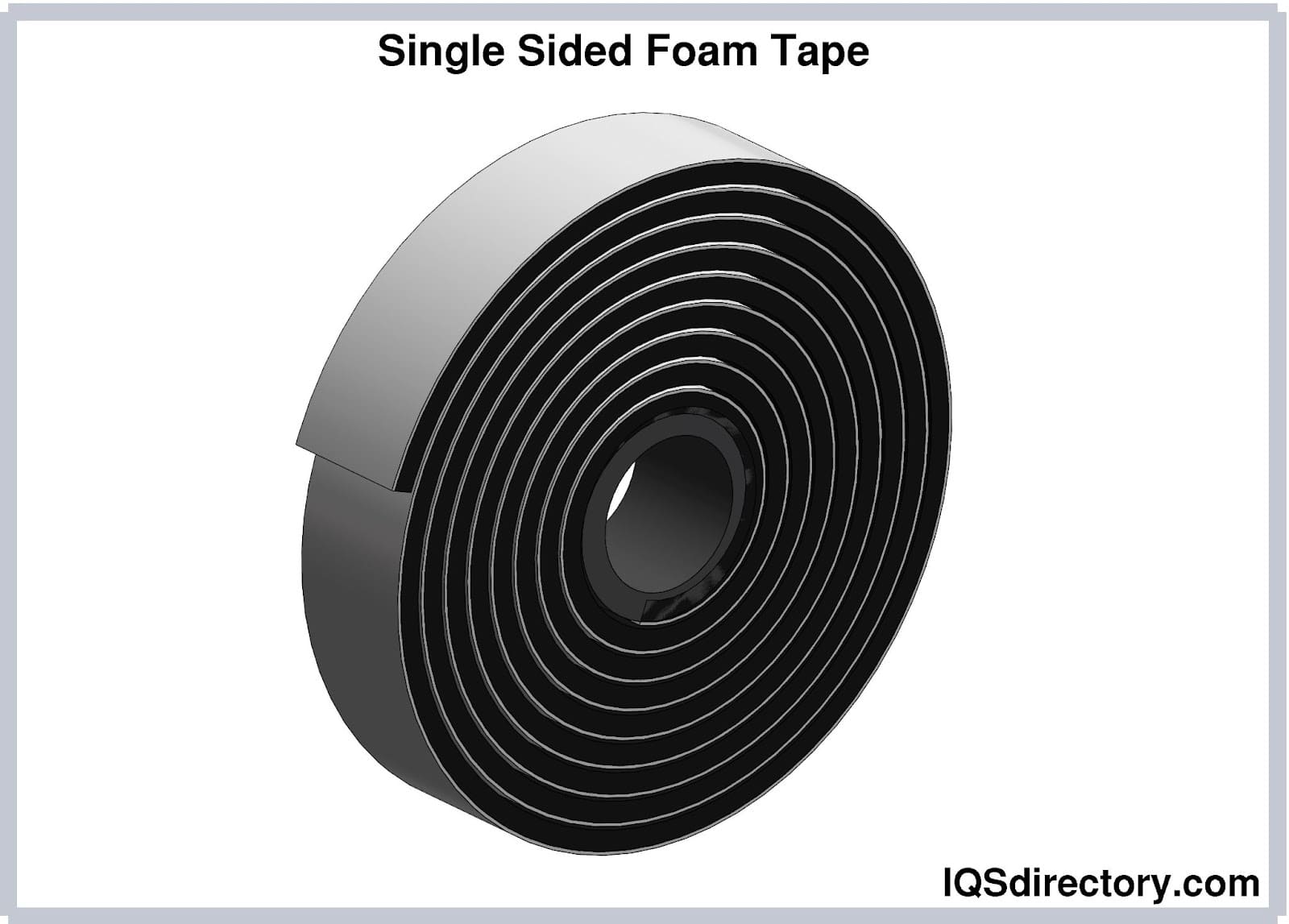
- Foam tape: Constructed from polyethylene or similar foams, foam tape offers cushioning, sound dampening, insulation, and gasketing. Its compressibility and weather-resistance make it valuable for HVAC, automotive, window, and door sealing applications.
- Vinyl tape (PVC tape): Recognized for stretchability and residue-free removal. Available in multiple colors, vinyl tape excels in safety marking, color coding, wire identification, and temporary surface protection. Its electrical insulating properties are leveraged in industrial and commercial settings.
- Foil tape: Made from aluminum or copper foils, foil tape offers high thermal conductivity, flame resistance, and EMI/RFI shielding. Used for sealing ductwork, HVAC systems, electrical shielding, and aerospace applications.
- PTFE (Teflon) tape: Used primarily for sealing threaded pipe joints, PTFE tape provides chemical resistance and leak-proof performance in plumbing, gas, and hydraulic systems.
Other Common and Specialty Tapes
- Gaffer’s tape: Heavy cotton cloth tape with a matte finish, gaffer’s tape is a staple in theater, film, and event production for securing cables and marking positions without leaving sticky residue.
- Marking tape: Used to designate areas, mark hazards, or guide equipment placement in manufacturing, construction, and logistics facilities.
- Sealing tape: Bonds joints or closes containers. Types include acrylic, hot-melt, and printable carton sealing tapes—ideal for logistics, shipping, and warehousing.
- 3M tape: Manufactured by 3M, these tapes (including Scotch Tape) feature advanced adhesives and are widely adopted in office, industrial, and specialty markets.
- Printed tape: Custom-printed with text, warnings, or branding for packaging, security, or instructional purposes.
- Acid-free tape: Lacks acidic content, making it safe for archival, conservation, and photo mounting. Frequently used by museums, galleries, and artists.
- Double-sided tape: Features adhesive on both sides, enabling invisible bonding in mounting, crafting, packaging, and signage. Some variants include removable liners for ease of application.
- Side tape (edge tape): Used to reinforce or provide grip on sports equipment, such as tennis racquets and hockey sticks.
- Paper tape: Lightweight, breathable, and hypoallergenic, paper tape is preferred in medical bandaging and other health-related uses.
Not sure which tape suits your needs? Ask yourself: What materials am I bonding? Will the tape be exposed to weather, chemicals, or heat? Does my application require high strength or easy removability? Explore tape supplier options or consult with our experts to find the ideal product for your requirements.
Accessories
Choosing the right tape accessories maximizes efficiency, precision, and safety in tape application. Critical accessories include:
- Scissors and cutting tools: Essential for trimming tape to exact lengths, especially for detailed tasks or heavy-duty tapes. Precision blades such as X-ACTO® knives are invaluable for crafts, model-making, and industrial prototyping.
- Marking tools: Allow for accurate line drawing or positioning on masking tape—crucial for painting, crafting, or technical installations.
- Applicators: Ensure even spreading of adhesives or other substances, reducing waste and improving consistency.
- Tape dispensers: Available in handheld, tabletop, or automated formats, dispensers enhance workflow efficiency by facilitating easy tape release and cutting. Industrial tape dispensers can handle large rolls and high-volume operations.
- Specialty sprays: Adhesive sprays improve bonding strength on difficult surfaces, while repositionable sprays allow for temporary tape placement and adjustment—particularly useful for signage, displays, and set design.
Wondering which tape accessory is right for your project? Consider the tape type, material, and level of precision required. For large-scale packaging, an industrial tape dispenser offers speed and reliability, while crafts and model-building benefit from fine cutting tools and applicators.
Standards
Quality assurance and performance consistency in tape products are governed by internationally recognized standards. Major benchmarks include:
- ISO Certification: Tapes certified under ISO (International Organization for Standardization) meet stringent requirements for quality, safety, and environmental management. ISO standards evaluate factors such as peel resistance, thermal stability, tensile strength, clean removal, and bonding reliability—ensuring tape products perform as promised in industrial and commercial contexts.
- ASTM International Standards: ASTM tests define key tape properties, including tensile strength, shear strength, adhesion, fracture toughness, and creep resistance. Certification provides buyers with objective, third-party validation of product performance and suitability for specific applications.
Searching for tape that meets high-performance criteria? Look for ISO- or ASTM-certified products when reviewing tape supplier catalogs, especially if your industry demands regulatory compliance or mission-critical reliability.
Things to Consider
With the vast variety of adhesive tapes on the market, selecting the right product for your application involves careful evaluation of your needs and available options. Here’s how to approach your tape purchasing decision:
- Identify your application: Consider whether you need tape for general repairs, industrial manufacturing, packaging, electrical work, or a specialty use. Define your performance requirements, such as strength, removability, or environmental resistance.
- Compare products: Review technical specifications, data sheets, and sample offerings from top tape suppliers. Assess factors like adhesion strength, carrier material, thickness, roll length, temperature range, and chemical resistance.
- Consider customization: If off-the-shelf products don’t fit your needs, inquire about custom tape manufacturing. Leading suppliers can tailor adhesive formulas, carrier materials, and roll dimensions to your operational requirements.
- Evaluate supplier credentials: Check for ISO, ASTM, or industry-specific certifications. Confirm the manufacturer’s capacity for quality control, timely delivery, and after-sale support.
- Request samples: Test sample tapes in your application to ensure compatibility and performance before committing to bulk orders.
For specialized or mission-critical bonding applications—such as aerospace, medical devices, automotive manufacturing, or electronics—partnering with an experienced contract tape manufacturer is highly recommended. These experts will guide you through adhesive selection, compliance requirements, and prototyping to guarantee your tape delivers optimal results under real-world conditions.
Ready to start your search for the perfect tape supplier? Explore our comprehensive list of tape manufacturers and distributors. Each company profile includes detailed information about their product lines, customization capabilities, industry certifications, and service offerings.
To narrow your options, select several suppliers that align with your needs and reach out directly to discuss your project requirements—covering standards, budget, lead times, and delivery logistics. After evaluating responses and samples, choose the partner that provides the best fit for your unique application.
Have questions about tape selection, supplier evaluation, or use-case scenarios? Contact our team or use our search tool to find answers and connect with leading tape industry experts. Your next adhesive solution is just a click away!
What are the main applications of adhesive tape?
Adhesive tape is used in a variety of industries and everyday tasks, including aerospace assembly, arts and crafts, automotive manufacturing and repair, packaging, construction, electrical insulation, furniture manufacturing, healthcare, food packaging, office supply, general manufacturing, painting, and sports and recreation.
How did adhesive tape evolve over time?
Adhesive tape has evolved from ancient glues used by early humans and civilizations to modern synthetic adhesives. Key developments include the creation of surgical tape in 1845, Band-Aid in 1921, masking tape in 1925, and duct tape in 1942. The industry has since expanded with specialty tapes for various demanding applications.
What are the main methods of manufacturing adhesive tape?
The primary manufacturing methods are water-based coating, solvent coating, and hot-melt coating. After adhesive is applied to a carrier, tapes may undergo converting processes such as slitting, die cutting, or printing, to ensure suitability for end-use.
What materials are used in tape manufacturing?
Common tape carrier materials include PVC, EPDM, PTFE, aluminum and copper foil, biodegradable materials like polylactic acid and cellulose acetate, paper, tissue, and films. Adhesives can be acrylic, rubber, silicone, hot-melt, epoxy, or specialty formulas customized for electronics or medical use.
How do I choose the right type of tape for my application?
To select the right tape, consider factors such as required adhesion strength, compatibility with surface materials, environmental exposure, desired size and form, color or printing needs, packaging, and relevant certifications. Testing samples in your application can help ensure the best choice.
What are common types of adhesive tapes and their uses?
Popular types include duct tape for repair and sealing, masking tape for painting and labeling, packaging tape for securing shipments, electrical tape for wire insulation, vinyl tape for marking, foil tape for shielding, gaffer’s tape for event production, double-sided tape for mounting, and more, each designed for specific functions and environments.
Which accessories improve tape application and safety?
Critical tape accessories include scissors and cutting tools, marking tools, applicators, tape dispensers, and specialty adhesive sprays. Choosing the right accessory depends on the specific tape and required precision for your project.
Why are standards important in tape selection?
Standards such as ISO and ASTM assure buyers of tape product quality, safety, and performance. Certified tapes are tested for strength, durability, thermal stability, and other criteria, ensuring reliability in critical and regulated industries.








 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services